Role of EA in cloud transformation
Any enterprise wide programs such as cloud transformation require clear strategic direction to succeed as planned.
Context
Any enterprise wide programs such as cloud transformation require clear strategic direction to succeed as planned. It is not surprising that, at times organizations will face challenges on where to start and lacks the strategic direction. Enterprise Architecture describes a high-level design of the structure of the organization, the roles, the processes and the functions, IT systems and IT infrastructure as well as their interrelationships, in order to realize the business goals and objectives. For a robust and coherent Enterprise Architecture it is necessary to use an EA framework. An EA framework is a set of structures for developing Enterprise Architectures. The EA frameworks contain guidelines, tools, common vocabulary and a method for designing the target state of the organization in terms of building blocks. Furthermore, they include a list of recommended standards and compliant products that used to implement the building blocks. For the very reason, the enterprise frameworks such as TOGAF would provide much needed bootstrap steps in very structured manner with definitive guidelines in each phase of the transformation journey. The EA teams would play pivotal role, as it owns the business outcome of the enterprise initiatives. This paper would outline role of enterprise architecture / frameworks in cloud transformation initiatives.
Iteration-0
In early stage of the program, organization has to form team that comprises key members who are responsible and part of advisory council to carry out enterprise initiative. The team might comprising IT heads, business owners, architects and any other members who knows the IT landscape of the company. This team is responsible for formally communicating to executive sponsors on every stage of the cloud transformation and its outcome. In this stage, team would describe / understand current IT landscape to support its business capabilities. As team understands/describes AS-IS state, it will also decides on strategic objectives of cloud transformations and high-level requirements for the program. The key outcome in initial stages is to decide on using EA frameworks and its tailoring etc. For example, tailoring of TOGAF ADM to suite specific program requirements and expected outcome.
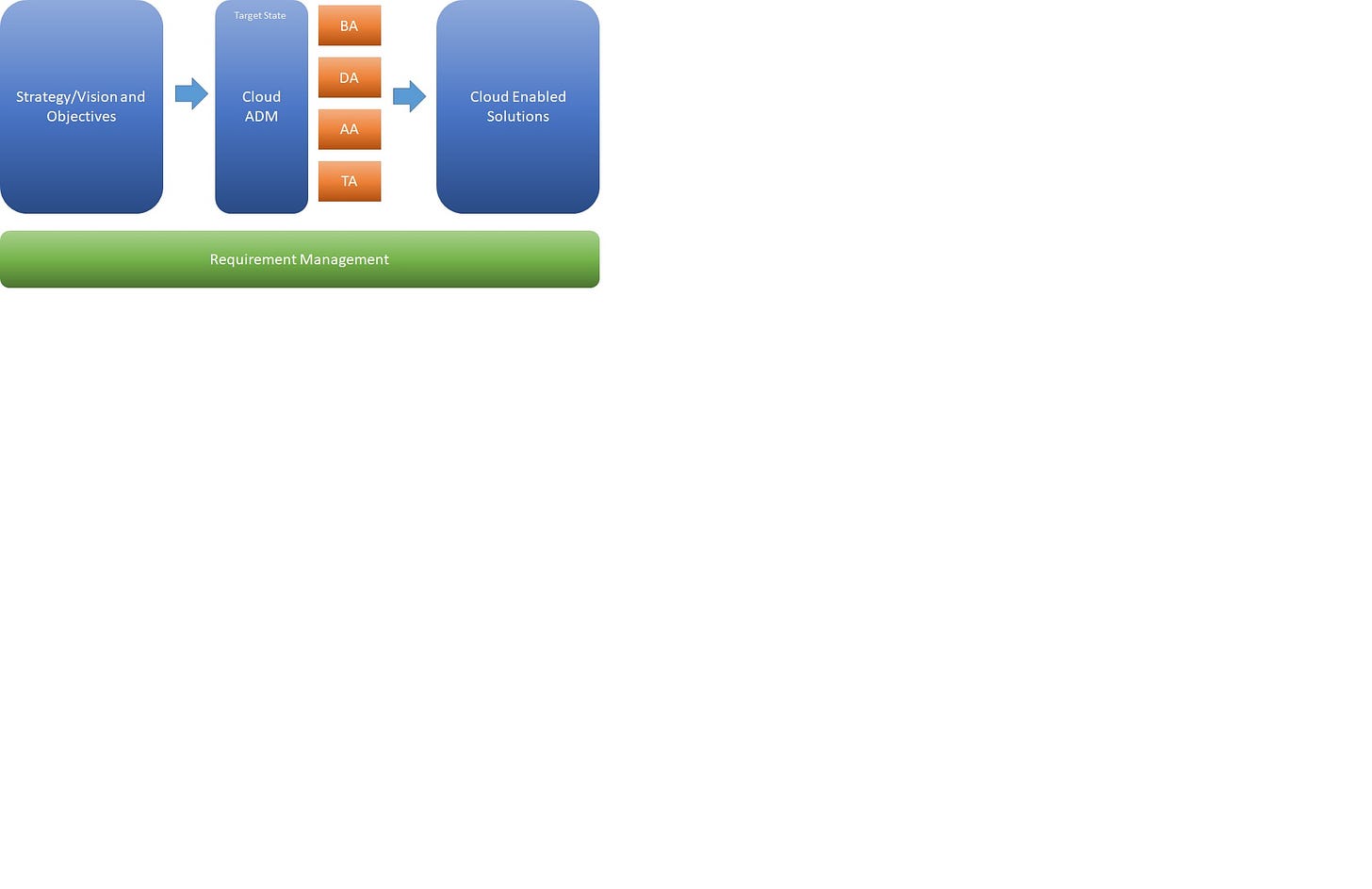
Cloud ADM
The standard TOGAF ADM (Architecture Development Method) steps reviewed and adopted for cloud architecture descriptions and executions. The TOGAF ADM divided into 3 distinct categories –
Strategy, Vision and Objectives
Core Architecture Execution Layer
Implementation, Migration and Governance
Not all the phases of ADM deemed necessary for each business context. For most of the small to medium scale program executions, minimalistic ADM – comprising Strategy, Vision, Motivation and Core Layer is just enough.
Preliminary & Architecture Vision
In this phase, the cloud adaptation strategy is developed. This includes-
Ø Design architecture vision for cloud transformation. For example- Replace on-premises data center is one such example that would define clearly business outcome of the initiative and how it benefits the organization future state.
Ø Development of architecture principles – Set of architecture principles relevant to cloud transformation described and presented. This will be guiding principles for future state architecture and key input to next phases of ADM. Below are such principles relevant to cloud transformation.
No technology proliferations
All applications in future state should be compatible to PaaS environment
All application specific databases should be migrated to cloud environment
All applications shall adhere to 99.99% up-time and available
Application scalability should be achieved using cloud provided services and shall be automatic
On-premises integration should follow Serverless architecture
Future state applications should follow cloud native services an deployment model
No direct communication between systems rather it would be via REST APIs
REST APIs would follow Open API specification standards
Ø The objectives and selection criteria for cloud service provider is designed and presented with executive sponsorship teams. This include critical costing model for large enterprise applications.
Ø Standardize the architecture assets and repository model - At this stage, the architecture continuum designed and methods of building repository structure and its presentations are discussed and baselined. The industry endorsed cloud reference architecture would provide a basis for architecture repository. The cloud specific taxonomy is prepared and made it available in shared document repository structures like Wiki. Each architecture artefacts are stored in centralized locations and links made available through Wiki pages.
Concisely, the objective is to identify cloud-specific capabilities, which aligned with the enterprise-wide strategy in order to leverage maximum value from the EA with low risk. The main activities of this phase to establish the scope of the architecture work, the creation of the strategic vision and the identification and prioritization of capabilities those realized in Core execution layer.
Design Cloud Architecture Domains
The design of core architecture domains holds key decisions on various architecture types on business, application, data and technology. The TOGAF ADM provides comprehensive guidelines and artefact catalogue to realize architecture domains.
Business Architecture
All the inputs from preliminary and vision phase is analyzed and enterprise wide business architecture for cloud transformation developed. The EA team would develop views specific to cloud migrations. One of the key activities in this phase to rationalize the enterprise application portfolio for future state. All strategic applications logically grouped and marked for its business importance. The gap analysis is prepared and non-strategic applications / capabilities are decommissioned. The comprehensive analysis / study is carried out to harness the cloud services in the form of SaaS, PaaS, IaaS or Serverless computing for each of the business services. In the process, organization shall identify new roles to manage the cloud services such as Cloud Management Teams, Cloud CoE, Cloud Governance Body etc., which is otherwise not present.
It is important to develop and baseline the impact analysis / value-add descriptions when business systems are developed / deployed in cloud managed services. The target business architecture would contain all findings of business objectives and its perceived benefits of moving to cloud environment. The BA phase is very critical as it provides more enhanced set of requirements, roadmaps to IT architecture realization.
IT Architecture
In ADM, the IT Architecture divided into 02 distinct architecture disciplines – Application Architecture and Data Architecture. At this stage, the organization data studied to identify its flow, storage and access environment, its importance respects compliance systems, data migration strategies – to retain on-premises or move to cloud are determined. Very detailed migration strategy designed that is compatible to target cloud deployment environment. The different data architecture views developed to validate and get buy-ins from key stakeholders who owns the data.
The impact analysis descriptions on data migrations over applications discussed and deliberated at this phase. This will result in detailed remediation steps / transformation notes for cloud transformation teams to carryout executions. As part of cloud transformation, applications largely categorized into - Rehost, Refactor, Revise, Rebuild or Replace. The decision matrix developed comprising of all the applications those stated for migration. The corresponding high-level costing model developed and presented to executive sponsors to align on revised costing. In most cases, costing would differ when realized in preliminary stages of EA development. Typically, cloud transformation teams would require very low-level artefacts on application migration those would involve like –
Legacy remediation steps for cloud deployment environment
Technology upgrades on target state as part transformation
Revised security/identity management approaches in cloud native environment
Re architect the solution(s) with modern architecture methodology such as Microservices
Cloud native deployment and release process for various stages of application verification cycle
Cloud service usages / its catalogue for specific usage scenario
Conversion of legacy Webservices to REST APIs etc. to have uniform design on API economy
Adoption of DevOps
The EA can advise cloud transformation / project teams to perform key technical spikes to validate few key decisions. The whole ADM is iterative in nature and can easily adopted using popular agile methodologies such as SCRUM with definitive sprint commitments.
At the end of this phase, 02 architecture artefacts are designed and baselined – Cloud Application Architecture and Cloud Data Architecture.
Technology Architecture
The inputs from previous steps assessed for gap analysis with cloud offering to realize different aspect of TA viewpoints. The Technology Architecture reveals the technology services strategy to address technical services requirements. It is also identified the logical and physical technical aspects of IaaS, PaaS, SaaS capabilities which support the business objectives. Then it is possible to realize cloud-based solution blocks in later phases of ADM and to redefine the solution architecture. A comprehensive assessment of the Baseline Technology Architecture will identify the technology gaps.
The TA would reveal the cloud characteristics of target state. The target TA is key and plays a major role in cloud enabled services. Many traditional architecture works made available out of the box by popular cloud providers such as availability, scale and security. Few key deliverables in this phase are –
Cloud infrastructure views for key applications with detailed decisions on availability, on-demand scalability options and security
Key cloud service catalogues mapped with application capabilities
Cloud region and location diagrams and network bandwidth / latency decisions
Tailored technology principles derived from overarching Architecture vision / principles
Management and Monitoring of cloud services and its SLAs
Target state architecture with decisions matrix for each of the gaps
Revised costing model and tagging of cloud resources associated with each business units
Cloud deployment models – Private, Public and Hybrid and also multiple cloud provider interoperability considerations
Realization
The realization of target architecture designed in three distinct phases – Opportunities & Solutions, Migration Planning and Implementation Governance. All inputs from previous target architecture domains analyzed and roadmap defined with help of multiple transition architectures. The target architecture building blocks converted to cloud enabled solutions. The optimal cloud enabled enterprise portfolio defined based on the gap analysis of baseline and target architectures. The projects, programs and portfolios identified to enable effective cloud transition roadmap. Typically, the project lifecycle in cloud ecosystem reduced significantly due to the rapid provisioning of services through SaaS, PaaS and IaaS and other out of the box services provided by cloud provider. The cloud transition architecture based on three primary implementation strategies.
Bespoke – Suitable for startup and small companies, which do not have existing infrastructure
Evolutionary – Gradual approach for moving from on-premises to target cloud environment. It is suitable for organizations that already have existing IT infrastructure and cannot afford any disruption. This is most common approach adopted by many large-scale transformation programs.
Revolutionary – Build and test everything in cloud and then switch completely to cloud during cut over. This is a high-risk option, not recommended options for large-scale transformations.
Each transition architecture should add business value to the organization. Following are the typical transition architectures –
On-premises->IaaS->TA1->TA2->PaaS
On-premises->Hybrid Cloud TA1…TAn->Full Cloud
On-premises->SaaS (Replace model)
The cloud transformation roadmap shall be logically grouped based dependent applications/services, geo specific data center decommissioning or business criticality of specific cloud capability / time to market.
The cloud migration plan defined with detailed project plans for each of application portfolio identified in transition architectures. The architecture governance model / body established to oversee and review the realization of transition architectures in migration/implementation step. The business value mapped with each work packages. In this phase, various business value metrics are generated and reviewed such as IT cost from Capex to Op-ex, SLAs in terms of availability, performance, on-demand scalability, provisioning of cloud services are compared with on-premises data centers. With cloud-enabled services, there is clear definition of cost of ownership is determined.
Finally, detailed architecture repository and transition architectures along migration plan is handed over to cloud solutions team to implement the solutions as per the guidelines/recommendations. The typical cloud solution implementation team would comprising cloud architects; devOps release engineers, application architects/developers and application owners. The immediate highly prioritized solutions are being developed. The Architecture review board would review the solutions for the stated business values, vision/principles and compliance. The entire implementation phase will be iterative in nature. Any architecture change request would trigger revisit of ADM phases to accommodate new changes and it is common in large-scale cloud transformations. The cloud transformation also enables enterprises to revamp the legacy technology stack with modern technology upgrades and architecture level refactoring to suite modern cloud native platforms. This will enable an increase in overall productivity, better maintenance and innovative services at scale.
Conclusion
A skillful adaptation of EA frameworks such as TOGAF would provide established structure for successful cloud transformations.